- TechForbs
- 0 Comments
- 8000 Views
- Introduction:
In today’s digital age, cloud computing has become the driving force behind the rapid transformation of businesses, from startups to Fortune 500 companies. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of cloud computing, shedding light on what it is, how it works, and the myriad ways it’s revolutionizing the way we store, manage, and utilize data.

What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that enables the delivery of computing services over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers and personal devices to manage data and applications, cloud computing allows users to access and store information on remote servers, often operated by third-party providers.
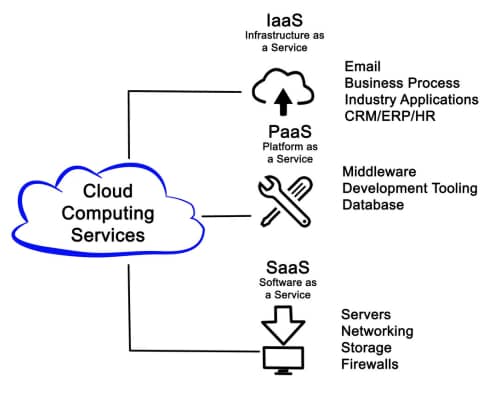
Types of Cloud Services
a. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, and networking.
b. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications.
c. Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications via the cloud, accessible through a web browser.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
a. Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for on-premises hardware and reduces maintenance and operational costs.
b. Scalability: Allows businesses to scale resources up or down as needed, avoiding overprovisioning.
c. Accessibility: Enables remote access to data and applications, fostering collaboration and productivity.
d. Security: Cloud providers invest in robust security measures, often exceeding what many organizations can achieve in-house.
e. Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based backup and recovery solutions offer a level of data protection that can be challenging to achieve with on-premises systems.
Common Use Cases
a. Data Storage and Backup: Cloud storage solutions provide scalable and cost-effective data backup and archival.
b. Web Hosting: Many websites are hosted in the cloud, providing reliability and scalability.
c. Software Development and Testing: Developers use cloud platforms for building, testing, and deploying applications.
d. Big Data and Analytics: Cloud services offer the computational power required for analyzing large datasets.
e. AI and Machine Learning: Cloud-based AI platforms provide access to cutting-edge machine learning tools and models.
Challenges and Considerations
a. Security and Privacy: Data security and compliance are crucial considerations when moving to the cloud.
b. Downtime and Reliability: Cloud service providers may experience outages, impacting business operations.
c. Data Transfer Costs: Moving large amounts of data in and out of the cloud can incur additional costs.
d. Vendor Lock-In: Businesses should consider how easily they can migrate from one cloud provider to another if needed.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing is not just a technological revolution; it’s a fundamental shift in the way businesses operate and leverage technology. Whether you’re a startup looking to scale rapidly, an established enterprise seeking cost-efficiency, or an individual in need of reliable data storage, the cloud has something to offer. Understanding the basics of cloud computing and its myriad applications is a crucial step in harnessing its power and potential for a brighter digital future.